What is KNX IoT Point API
Introduction
The KNX IoT Point API is an extension of the suite of KNX physical transmission medias. The KNX IoT Point API is part of KNX IoTech as part 3.10.5. The transmission media is IPv6 hence future proofing KNX and can be used on a variety of phyiscal transports. The KNX IoT Point API products can be used with existing KNX products in a single system. For example it can be combined with existing product on Twisted Pair (TP), KNXnet/IP using IPV4 and KNX-RF using radio transmission on 868 MHz. KNX IoT Point API is an evolution of the KNX system and being IPv6 it can be used with various networking mechanisms.
The most common usage of KNX is using the TP variant using cables.
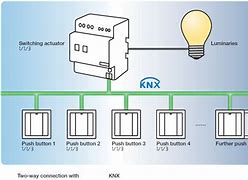 |
|---|
| KNX bus diagram |
Resulting in using large cabinets to hook up all the devices.
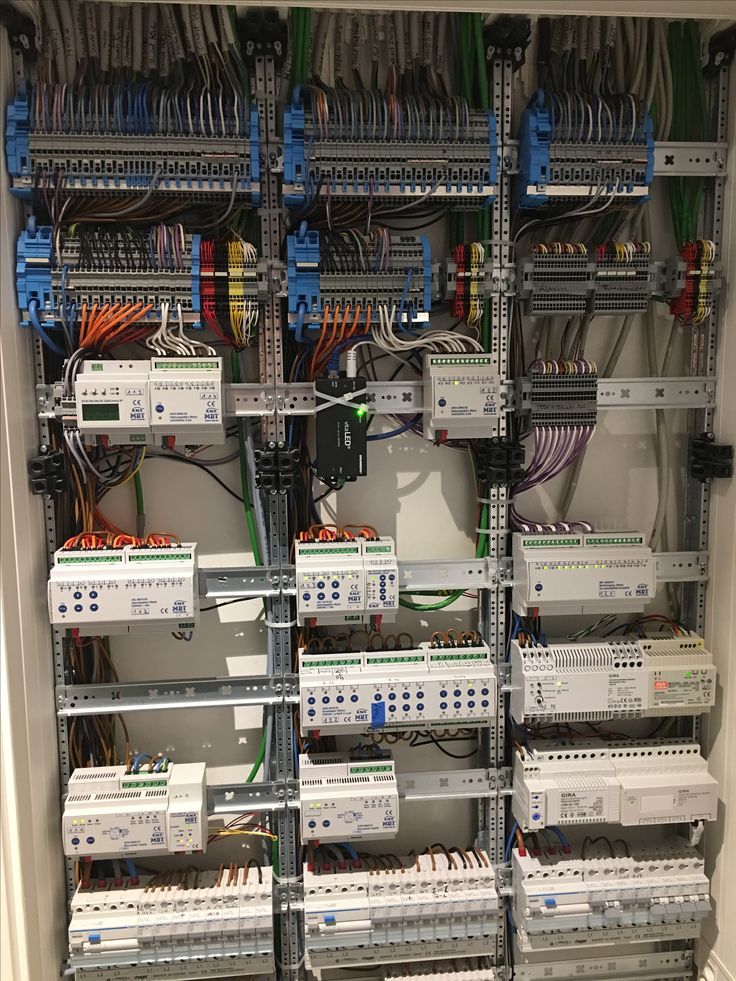 |
|---|
| KNX cabinet |
The most interesting one is Thread, capable of creating a large area, wireless meshed IPv6 network. Using Thread-based devices will reduce the typical KNX bus wiring.
Articles on KNX today
KNX IoT: Part 1 – an introduction – KNXtoday
KNX IoT: Part 2 – the advantages of Thread – KNXtoday
KNX IoT: Part 3 – the fundamentals of KNX IoT devices – KNXtoday
KNX IoT: Part 4 – the architecture of KNX IoT devices – KNXtoday
KNX IoT: Part 5 – creating a heterogeneous installation by using a KNX IoT Route
KNX IoT: Part 6 – Using Thread for KNX IoT
KNX IoT: Part 7 – the open-source KNX IoT stack
Technical Background
KNX IoT Point API is a new specification in the KNX system specifications group (see 3_10_5 KNX IoT Point API.)
The specification describes:
- A new transport layer based on IPv6, e.g. suitable for Thread-based networks.
- A new communication/message protocol using CoAP and CBOR.
- Using the same functional blocks as the other KNX transport layers.
- Using the same s-mode message semantics as the other KNX transport layers.
- Using the same configuration data to configure which device is talking to which device.
Hence KNX IoT Point API conveys the same semantic data on the transport layer as a KNX TP implementation. therefore the interworking between KNX IoT Point API and the other KNX technologies is garanteed.
Functional Blocks / Data points
The application domain in KNX is described by functional blocks (FB). The Functional Blocks are a consistent set of data points that describe the domain. There can be mandatory and optional data points in a functional block. Functional Blocks are described in the KNX specification volume 7: Application descriptions.
An example of a functional block is Light Switching Sensor Basic (LSSB), which provides hardwired inputs or local push-button/HMI functionality to trigger output messages to control the On/Off status.
Since the LSSB is a Sensor, it sends out the triggers to the Actuators FB Light Switching Actuator Basic (LSAB) or FB Light Dimming Actuator Basic (LDAB). Next to the data point that sends out these triggers, there is another data point that receives status feedback messages from light switching/dimming actuators.
How the actual function of the system is configured across the devices is achieved by the configuration data.
Note: You will come accross the term “resource” in this documentation. This word is used synonymously with “data point”, so they are interchangeable in the context of KNX IoT.
Configuration Data
For sensor data points, the Management Client (MaC) needs to set up the following in the Group Object table:
- Which group address is being used to send the data
- The href, which identifies a data point
- Whether the device is allowed to send the message (cflags, e.g. “t”)
For the actuator data points, the Management Client (MaC) needs to set up:
- Which group address is being used for receiving the data
- The href, which identifies a data point
- Whether the data is to be interpreted (acted upon) by the device (cflags, e.g. “w”)
IPv6
IPv6 can run over different cables and can be used wirelessly. Ethernet cables like CAT6 can be used for wired networking, and PoE (Power over Ethernet) can also be used to power devices connected via Ethernet cables. Next to wired solutions, IPv6 can run over Wi-Fi and Thread-based networks.
What is new
- The KNX IoT Point API is secured (on Application layer) by default.
- Mandatory software update mechanism included.
How to combine KNX TP and KNX IoT Point API
Since KNX IoT is semantically equivalent to another KNX transport layer, interworking between KNX IoT Point API and KNX/TP and KNXnet/IP is possible through an knx iot router.
The knx iot router converts messages from KNX/TP (or KNXnet/IP) to KNX IoT Point API messages.
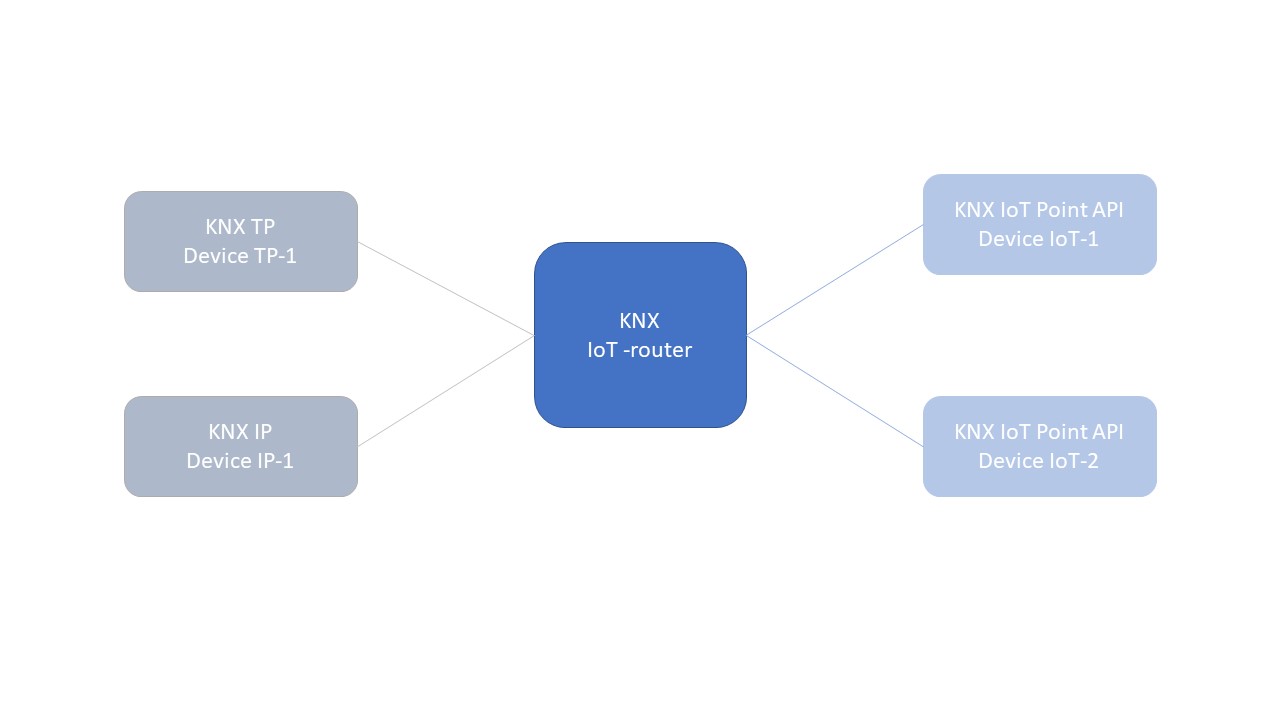 |
|---|
| KNX IoT Router |
What are the advantages of KNX IoT Point API?
The advantages of KNX IoT Point API is that the new technology is IPv6-ready and is using the latest (newest) IETF technologies in the specifications. The stack implementing the KNX IoT Point API therefore is quite small and can run on MCU devices with only 100kb of memory. KNX IoT Point API is also secure by design, due to the usage of the latest IETF technologies in the specification.
Thread based devices can be made with KNX IoT Point API. Advantages of Thread are:
- Meshed networking, e.g. covering a large area.
- Using the same radio across the world, e.g 1 product that can be used/sold in all regions of the world.
- Low power end devices, which can go to sleep and reattach to the network when waking up.